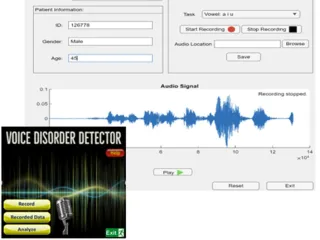
Voice disorder detection has gained considerable attention in the field of machine learning research. While previous studies have primarily focused on distinguishing between healthy and pathological voices, only a few have explored the classification of multiple voice disorders. In this innovative approach, a hierarchical Support Vector Machine (SVM) with additional features is proposed to accurately identify non-organic voice disorders. To overcome challenges and mitigate the risks of overfitting, the researchers employed k-fold cross-validation and spectral parameters in their methodology. This ensured robustness and reliability in the classification process. The use of k-fold cross-validation allowed for comprehensive model evaluation by partitioning the dataset into multiple subsets, training the model on a subset, and testing it on the remaining subsets. By repeating this process multiple times, the performance of the classifier could be effectively assessed. One of the key elements in the proposed method is the utilization of Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) as a feature for voice analysis. MFCC is a representation of the short-term power spectrum of a sound, which has been widely used in speech and audio processing applications. It captures essential characteristics of the voice, such as timbre and pitch, by analyzing the spectral content of the sound. The experimental results of this innovative approach were impressive. The accuracy achieved for distinguishing between healthy voices and hypo functional dysphonia reached an impressive 98.98%. Furthermore, the classification accuracy for distinguishing between functional dysphonia, psychogenic dysphonia, dysodie, and dysphonie ranged from a minimum of 70.73% to higher values. The hierarchical SVM employed in this approach is a variant of the standard SVM classifier that allows for a more structured decision-making process. It hierarchically organizes the classes of voice disorders, enabling a step-by-step classification approach. This hierarchical structure helps reduce complexity and improve the accuracy of the classification task. By addressing the challenges associated with non-organic voice disorder classification and effectively mitigating the risks of overfitting, this innovation provides a promising solution for the accurate identification of voice disorders. The use of MFCC as a spectral parameter and the incorporation of hierarchical SVM further enhance the effectiveness of the classification system. The implications of this innovation are significant, as it can contribute to the early detection and diagnosis of non-organic voice disorders. Early identification of these disorders is crucial for timely intervention and treatment, leading to improved patient outcomes. Additionally, the proposed approach opens avenues for further research in the field of voice disorder detection and classification, stimulating the development of more advanced and accurate systems. Therefore, the classification of non-organic voice disorders using Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) and hierarchical SVM demonstrates promising results. By leveraging spectral parameters and addressing challenges associated with classification, this innovation provides a reliable and effective method for detecting and distinguishing between various non-organic voice disorders.




Comment