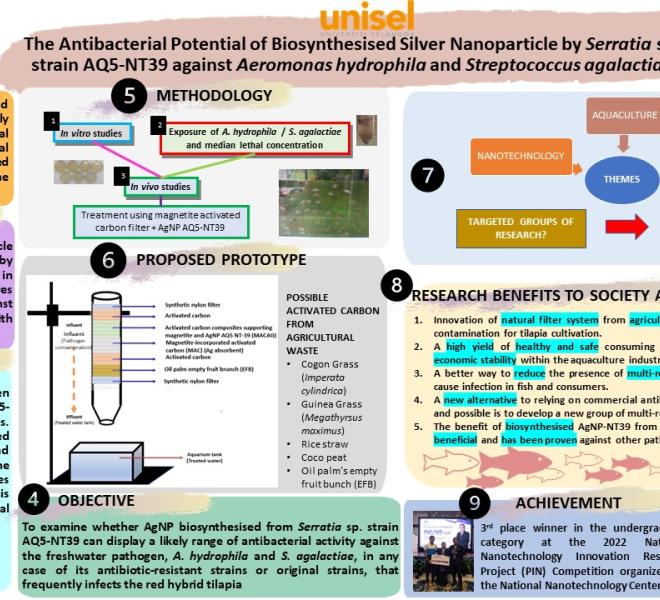
Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae, have posed a threat and contributed to the rise of antimicrobial resistance evidence of impacting the tilapia farms, particularly Oreochromis niloticus x O. mossambicus (red hybrid tilapia fish). Nevertheless, a previously studied marine bacteria, Serratia sp. strain AQ5-NT39 has proved to synthesise AgNP biologically due to the tolerance to heavy metals and possess more favourable antibacterial capacity against marine pathogens, Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio harveyi are hypothesised to combat the A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae infections. This research study the antibacterial potential of the biosynthesised AgNP by Serratia sp. strain AQ5-NT39 against A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae. The antibacterial action of the biosynthesised AgNP at the in vitro and in vivo scale was observed. The obtained Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) value of AgNP was used to treat the infected water with the value of obtained median lethal concentration (LC50). This characteristic shows potential to be used in a filtration system. The value through a magnetite-activated carbon (MAC) + AgNP AQ5-NT39 (MACAG) treatment by enhancing the mechanical features and antibacterial properties against infected red hybrid tilapia with these pathogens. These filter applications were influenced but with slight modifications by previous research (Sarkheil et al. (2016); Valušová et al. (2012)). Adding silver absorbent (MAC) in the filter column decreased the release of silver from the filter column into seawater. This filter column's utilisation for red hybrid tilapia cultivation could improve the fish's survival rate and growth performance compared with the infected water tank. The addition of oil palm's empty fruit bunch (EFB) consists of hard, abundant, and multicellular solid fibres. The EFB morphology makes it suitable for biosorption, and it has been reported that this eco-friendly material is widely used to biosorp heavy metals and dyes (Puasa et al., 2022). The results indicated that immobilised AgNP AQ5-NT39 onto MAC substrates, according to the described method by Valušová et al. (2012), could be used as a suitable antibacterial agent in the aquaculture industry. Activated carbon was impregnated with magnetite (MAC) and exhibited high efficiency in adsorption with Ag+ions. The positive surface charge appears to play a major role in the adsorption of bacteria. The magnetic properties of MACAG composites allow them to be removed easily from water after the bactericidal effect. These initial results indicate that MACAG may have a potential application as a surface water disinfectant. Subsequent MACAG treatment resulted in decreasing silver concentrations. The possible sources of activated carbon were suggested using agricultural waste used to study oil spill filtration, which contained specific microscopic morphology and structure . The sources are cogon grass (Imperata cylindrica) (Khalid et al., 2021), Guinea grass (Megathyrsus maximus) (Khalid et al., 2023), rice straw (Taufik et al., 2021), coco peat (Verasoundarapandian et al., 2021) and EFB (Puasa et al., 2022). Hence, the in vitro and in vivo antibacterial action of the biosynthesised silver nanoparticles by Serratia sp. AQ5-NT39 against freshwater pathogens, plays an essential role in enhancing the mechanical features and antibacterial properties using the modified version of the filter system.







Comment